In a network with multiple voltage
sources, the current in any branch is
the sum of the currents which would
flow in that branch due to each
voltage source acting alone with all
other voltage sources replaced by
their internal impedances.
The goal of folowing text is to check
superposition theorem.
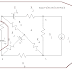
Step 1. Construct following circuit
using Circuit Magic then run Node
Voltage Analysis. (popular circuits
analysis technique). You can
alsocalculate currents using other
techniques.

Electrical scheme
Inital variables
R2=10Ohms; R1 =10Ohms;
R3 =10Ohms;
E1 =3V; E3 =4V;
Solution
V1 ·G11=I11
G11=1/R1 +1/R2+1/R3=0,3
I11 =-E1/R1 -E3 /R3 =-0,7
0,3V 1 =-0,7
V1 =-2,3333
V2 =0
I1 =(V1 -V2 +E1)/R1 =0,0666667
I2=(V1-V2)/R2 =-0,233333
I3=(V1-V2+E3 )/R3=0,166667
These values are used to check
currents determined from
superposition theorem
Step 2. Remove a voltage source
from the third branch then run
Node Voltage Analysis.

Electrical scheme
Inital variables
R2=10Ohms; R1 =10Ohms;
R3 =10Ohms;
E1=3V;
Solution
V1 ·G11=I11
G11=1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3=0,3
I11 =-E1 /R1 =-0,3
0,3V 1 =-0,3
V1 =-1
V2 =0
I1(1) =(V1 -V2 +E1)/R1 =0,2
I2(1) =(V1 -V2 )/R2 =-0,1
I3(1) =(V1 -V2 )/R3 =-0,1
These values are used to
determine current from
superposition theorem.
Step 3. Remove a voltage source
from the first branch then run
Node Voltage Analysis.

Electrical scheme
Inital variables
R2=10Ohms; R1 =10Ohms;
R3 =10Ohms;
E3=4V;
Solution
V1 ·G11=I11
G11=1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3=0,3
I11 =-E3 /R3 =-0,4
0,3V1 =-0,4
V1 =-1,3333
V2 =0
I1(2) =(V1 -V2 )/R1 =-0,133333
I2(2) =(V1 -V2 )/R2 =-0,133333
I3(2) =(V1 -V2 +E3)/R3 =0,266667
Superposition theorem checking
I1 =I1(1) +I1(2) =0,2-0,133333=0,0666666
I2 =I2(1) +I2(2) =-0,1-0,133333=-0,233333
I3 =I3(1) +I3(2) ==-0,1+0,266667=0,166667








0 comments:
Post a Comment